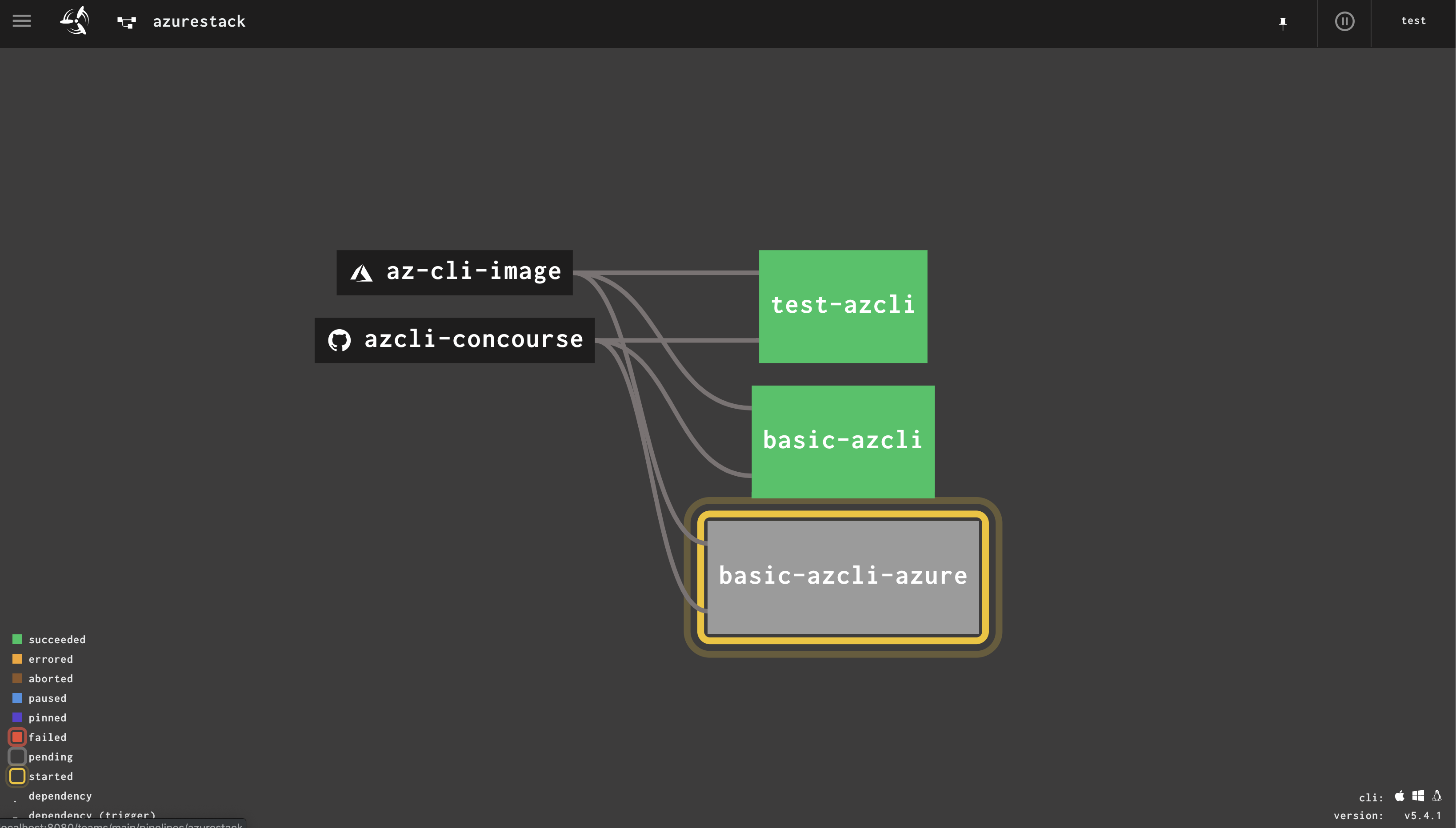
Use Concourse CI to automate Azure and AzureStack - Chapter 3 - working with Scripts, Tasks and Anchors
This Chapter will we will create out first Task that let us
- use Anchors to streamline pipelines
- create some tasks
- write a short script in a second Pipeline
Tasks and Anchors
First of all, we copy last weeks 03-azcli-pipeline.yml into 04-azcli-pipeline.yml
The first new task we are going to create should list all vm´s in a given resource group. Therefore, copy the basic-task.yml in your tasks folder to get-vms-rg.yml We will use the same Parameter set to initialize Azure/AzureStack, but this time we also need to add a parameter for the resource group.
edit the parameter section in the taskfile and add
RESOURCE_GROUP:
right under AZURE_CA_PATH.
In the run Part, right under az account set –subscription ${AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID}, add the following code:
az vm list --resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} --output table
you new Task File should look like this now:
---
# this a task to get vm´s of a certain resource croup
platform: linux
params:
PROFILE:
CLOUD:
# AzureStack AzureCloud AzureChinaCloud AzureUSGovernment AzureGermanCloud
CA_CERT:
ENDPOINT_RESOURCE_MANAGER:
VAULT_DNS:
SUFFIX_STORAGE_ENDPOINT:
AZURE_TENANT_ID:
AZURE_CLIENT_ID:
AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET:
AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID:
AZURE_CLI_CA_PATH:
RESOURCE_GROUP:
run:
path: bash
args:
- "-c"
- |
set -eux
case ${CLOUD} in
AzureStackUser)
if [[ -z "${CA_CERT}" ]]
then
echo "no Custom root ca cert provided"
else
echo "${CA_CERT}" >> ${AZURE_CLI_CA_PATH}
fi
az cloud register -n ${CLOUD} \
--endpoint-resource-manager ${ENDPOINT_RESOURCE_MANAGER} \
--suffix-storage-endpoint ${SUFFIX_STORAGE_ENDPOINT} \
--suffix-keyvault-dns ${VAULT_DNS} \
--profile ${PROFILE}
;;
*)
echo "Nothing to do here"
;;
esac
az cloud set -n ${CLOUD}
az cloud list --output table
set +x
az login --service-principal \
-u ${AZURE_CLIENT_ID} \
-p ${AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET} \
--tenant ${AZURE_TENANT_ID}
# --allow-no-subscriptions
set -eux
az account set --subscription ${AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID}
az vm list --resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} --output table
Commit your changes
git add tasks/get-vms-rg.yml
git commit -a -m "added get-vms-rg"
git push
adding the task to our pipeline and create anchors
The call of the task from the pipeline will essentially look like our basic task, just we have to add a parameter and change the name of the taskfile. as this will create a lot of overhead in the Parameters, we create a YAML anchor for our “Standard” Parameters of the task.
At the beginning of our 04-azcli-pipeline.yml, create the following Anchor: (it should name your environment, in my case, the asdk, so azurestack_asdk_env)
azurestack_asdk_env: &azurestack_asdk_env
CLOUD: ((asdk.cloud))
CA_CERT: ((asdk.ca_cert))
PROFILE: ((asdk.profile))
ENDPOINT_RESOURCE_MANAGER: ((asdk.endpoint_resource_manager))
VAULT_DNS: ((asdk.vault_dns))
SUFFIX_STORAGE_ENDPOINT: ((asdk.suffix_storage_endpoint))
AZURE_TENANT_ID: ((asdk.tenant_id))
AZURE_CLIENT_ID: ((asdk.client_id))
AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET: ((asdk.client_secret))
AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID: ((asdk.subscription_id))
AZURE_CLI_CA_PATH: "/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/certifi/cacert.pem"
in our existing Task fo AzureSTack, we replace the parameters in the params section with
params:
<<: *azurestack_asdk_env
now mark and copy the the basic task of your pipeline file.
insert it as a new task. change the task name to get-vms-rg, and change the path of the task file to get-vms-rg.yml Add a Parameter for the Resource Group, in my case asdk.resource group the new task should look like this: (note, i am using the parameters with prefix asdk. in this example as this is my set of specific parameters for my asdk)
- name: get-vms-rg
plan:
- get: azcli-concourse
trigger: true
- get: az-cli-image
trigger: true
- task: get-vms-rg
image: az-cli-image
file: azcli-concourse/tasks/get-vms-rg.yml
params:
<<: *azurestack_asdk_env
RESOURCE_GROUP: ((asdk.resource_group))
The Anchor will instruct fly to insert the Section from the Anchor definition edit the Parameter file to include the resource_group parameters:
asdk:
tenant_id: "your tenant id"
client_id: "your client id"
client_secret: "your very secret secret"
subscription_id: "your subscription id"
endpoint_resource_manager: "https://management.local.azurestack.external"
vault_dns: ".vault.local.azurestack.external"
suffix_storage_endpoint: "local.azurestack.external"
cloud: AzureStackUser
profile: "2019-03-01-hybrid"
azure_cli_ca_path: "/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/certifi/cacert.pem"
ca_cert: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
<<you root ca>>
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
resource_group: "you resource group"
save the files
Load the updated pipeline
we load Version 4 of our Pipeline now with
fly -t docker set-pipeline -p azurestack -c 04-azcli-pipeline.yml -l parameters.yml 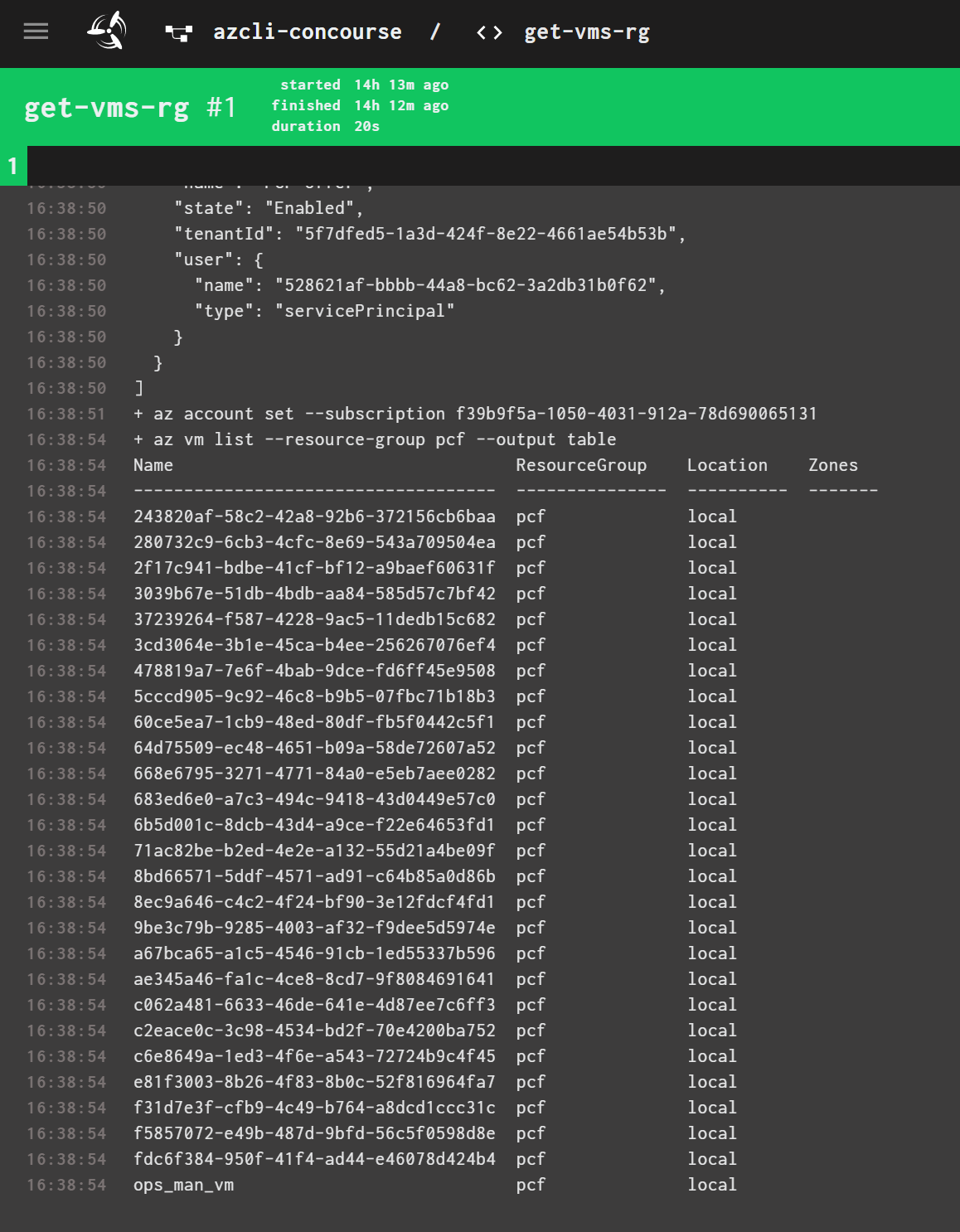
You may now create / apply anchors and tasks for your different Azure/AzureStack Environments
Do I need to write a task file each and every time ?
No, you do not have. Originally, the run Part of the task was Part of the Pipeline as well. And for testing Purposes, i would even recommend to create a short test-pipeline for you task including the run statement. That would allow you for easier testing and scripting WITHOUT applying changes to your master pipeline.
Example
create a pipeline file called script-test.yml .
Put in your Anchor(s). We do not need resource definitions, as we even call the image to use from within the Task. We to not trigger the job, as we want to run it manually.
This is a basic task i user for script testing. Modify the run section to your needs.
---
# script developement pipeline
azurestack_asdk_env: &azurestack_asdk_env
CLOUD: ((asdk.cloud))
CA_CERT: ((asdk.ca_cert))
PROFILE: ((asdk.profile))
ENDPOINT_RESOURCE_MANAGER: ((asdk.endpoint_resource_manager))
VAULT_DNS: ((asdk.vault_dns))
SUFFIX_STORAGE_ENDPOINT: ((asdk.suffix_storage_endpoint))
AZURE_TENANT_ID: ((asdk.tenant_id))
AZURE_CLIENT_ID: ((asdk.client_id))
AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET: ((asdk.client_secret))
AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID: ((asdk.subscription_id))
AZURE_CLI_CA_PATH: "/usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/certifi/cacert.pem"
jobs:
- name: script-test
plan:
- task: script-test
config:
platform: linux
params:
<<: *azurestack_asdk_env
RESOURCE_GROUP: ((asdk.resource_group))
image_resource:
type: docker-image
source: {repository: microsoft/azure-cli}
outputs:
- name: result
run:
path: bash
args:
- "-c"
- |
set -eux
case ${CLOUD} in
AzureStackUser)
if [[ -z "${CA_CERT}" ]]
then
echo "no Custom root ca cert provided"
else
echo "${CA_CERT}" >> ${AZURE_CLI_CA_PATH}
fi
az cloud register -n ${CLOUD} \
--endpoint-resource-manager ${ENDPOINT_RESOURCE_MANAGER} \
--suffix-storage-endpoint ${SUFFIX_STORAGE_ENDPOINT} \
--suffix-keyvault-dns ${VAULT_DNS} \
--profile ${PROFILE}
;;
*)
echo "Nothing to do here"
;;
esac
az cloud set -n ${CLOUD}
az cloud list --output table
set +x
az login --service-principal \
-u ${AZURE_CLIENT_ID} \
-p ${AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET} \
--tenant ${AZURE_TENANT_ID}
# --allow-no-subscriptions
set -eux
RESULT=$(az vm list --output json)
echo $RESULT
echo $RESULT > ./result/result.json
Now start a new pipeline called script-test with the new Pipeline file
fly -t docker sp -p script-test -c .\script-test.yml -l .\parameters.yml
The new Pipeline should be in a paused mode. Press the Play Button to start
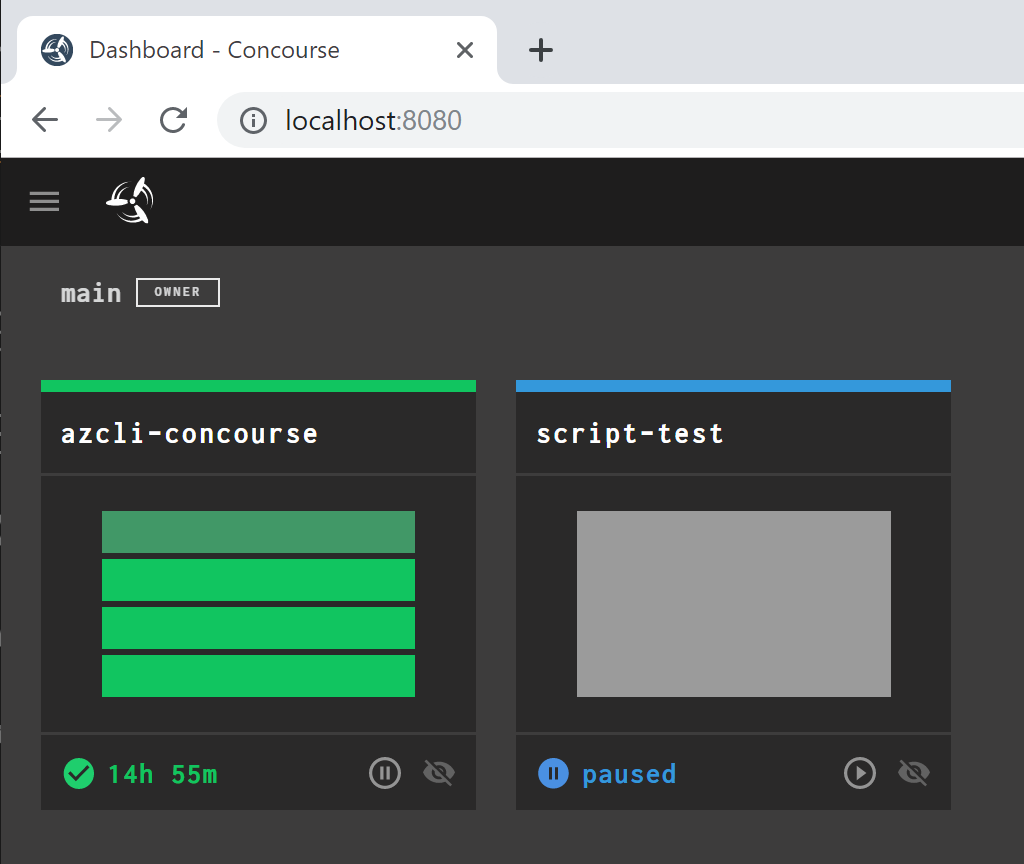
when you click in the script-test pipeline, you will see only one job, no dependencies, no triggers. Trigger a build by clicking the plus button
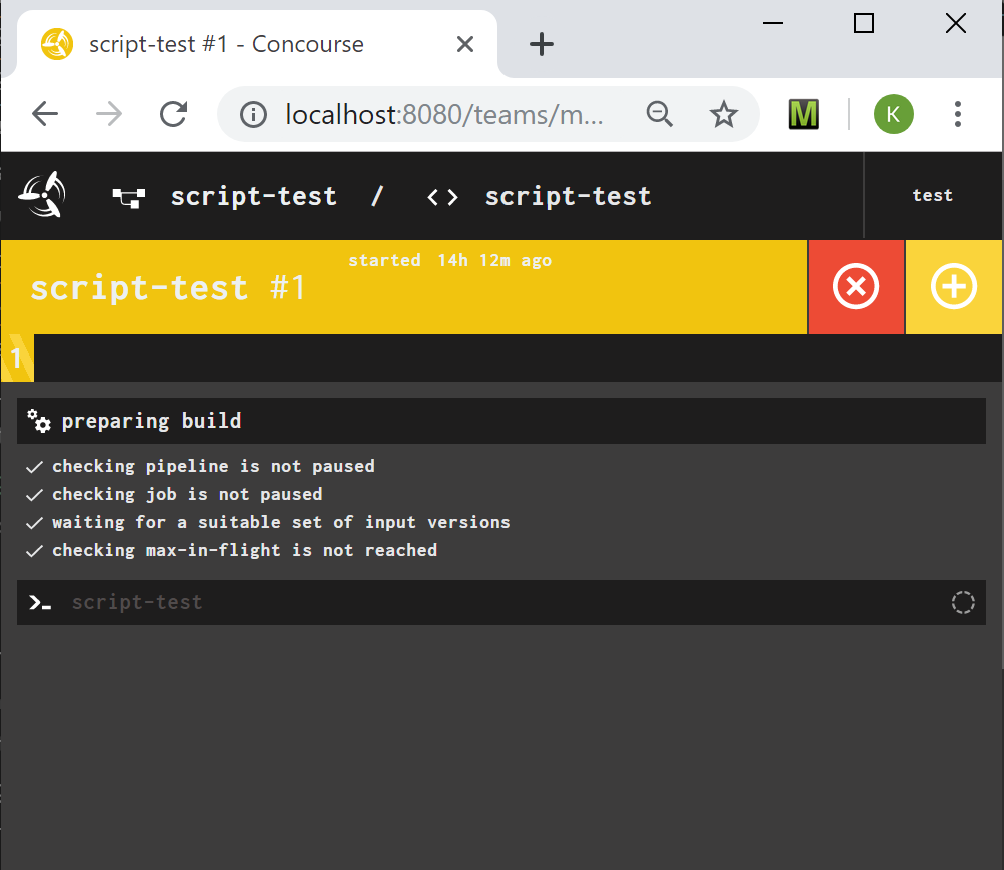
This should run your script.
You can see from the pipeline file that inline Scripting makes you pipeline quite large.
My preferred method is to put the scripts in task files and load them from GitHub.
You even can have versioned scripts zipped on external resources.
That will also allow to trigger a new build on script change.
We will dive into that in one of the next Chapters.
For now, familiarize yourself with Anchors, internal and external tasks, and even have a look at the fly cli for method´s to pass tasks from directories